Physio talks: Back Injury – Herniated Disc – Surgery and Physiotherapy options.
Physioactive presents the Singapore Surgeon Insight series with Dr. Hee Hwan Tak of Pinnacle Spine and Scoliosis Centre Singapore where he explains a specific back injury, the herniated disc, also known as the herniated nucleus pulposus.
Dr Hee Hwan Tak
Dr. Hee, an orthopedic surgeon specializing in spine and scoliosis surgery, explains the herniated disc, pre-and post-op regimens, along with the surgical procedure involved.
What is a herniated disc?
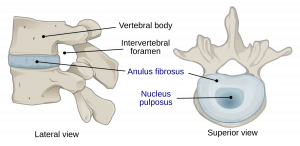
Nucleus Pulposus and Anulus Fibrosus
- The human anatomy explained: Intervertebral Disc
- A structure located between the bones of the spine or the Vertebrae(33 individual, interlocking bones that form the spinal column) of the spine
- Functions: shock absorber, provides flexibility to move, bend and twist the back
- Comprise of 2 microstructures
- Inner structure – Nucleus Pulposus – filled with water that provides shock-absorbing properties
- Outer structure – Annulus Fibrosus – gives rigidity and contains the nucleus in the right place
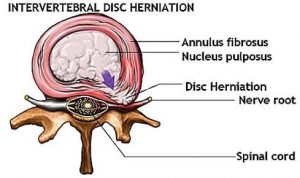
Invertebral Disc Herniation
-
- As we age/injury happens, to disc – there is a tear – annular tear – allows the material inside the disc to protrude out and irritate the nerve.
- The degree of irritation varies depends on the protrusion:
- Mild – Back pain and minimal leg symptoms
- Severe – pains, pins and needles, and loss of strength
- Most severe – loss of bladder or bowel control
- Commonly seen in age 30-50
- Less common in much older age group more than 50 because the disc is often dehydrated, therefore there are fewer chances of the protrusion. Hence, nerve comprehension source comes from other surrounding structures like the ligament, facet joint, or misalignment of the bone
When to seek medical attention with a herniated disc?
-
- Symptoms of HNP that rings an alarm to seek medical attention
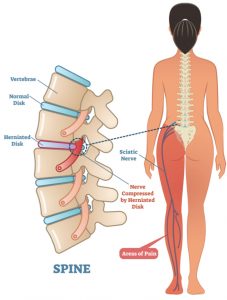
Pains associated with disc herniation
- Any neurological symptoms radiating down the leg – glute, thigh, or foot
- Pins and needles over various parts of legs
- Loss of feeling/sensation
- Gait problems due to weakness
- Symptoms over both legs more significant than on one leg
- Difficulty sleeping
- Loss of bladder control
- Patient concerns
- Is the condition serious?
- Will it lead to loss of mobility?
- Will I need surgery?
- After investigation, what can you offer me to get to what I was before?
- Symptoms of HNP that rings an alarm to seek medical attention
Surgical Intervention
-
- An indication that warrants surgical intervention
- Absolute indications – Immediate surgery needed!
- Of Bladder and bowel control – surgery within 48 hours
- Loss of motor power – foot drop from L4 L5 herniated disc leading to disfunction of L5 nerve root – causing not being able to walk on heels, balance issues
- Relative indications – consideration of surgery but not mandatory to do ASAP
- Failure of conservative treatments like medication, physiotherapy, lifestyle changes
- Negative impact on the quality of life, productivity, and recreational activities
- Patients want to improve further
- Worsening despite conservative treatments
- Absolute indications – Immediate surgery needed!
- An indication that warrants surgical intervention
Types of surgical procedures
-
-
- Procedure in between conservative and surgery
- Spinal Injection
- Cases not severe enough for surgery
- Done under sedation – anesthesiologist will be involved and local anesthesia to the local area
- Image guidance – a mobile x-ray to guide the position of the needle to the designated area
- Downtime: Day procedure – discharged on the same day
- Injection to the nerve being compressed
- Aim: reduce inflammation of the nerve
- It is not a stand-alone treatment – it’s a multi-disciplinary approach to combine with other treatments – Physiotherapist can handle patient better after the injection
- The procedure may not be long lasting
- Percutaneous Nucleoplasty – if disc prolapse is not too large
- Apply radio frequency to reduce nerve irritation
- The amount of reduction is limited
- Surgery
- Check with Dynamic x-ray –
- If there is no instability/misalignment of the spine then Keyhole surgery is a better option as it doesn’t destroy or damage normal structures in the spine
- If there is a misalignment of the spine (a condition called Spondylolisthesis), this would entail a more major procedure that should be discussed
- Keyhole surgery
- A minimal week stay in Singapore:
- Pre-operative surgery check-up, consent taking, explanation
- 1-3 nights hospitalization
- Post-discharge follow-up, dressing change, and inquiries
- Wound take 2-3 weeks to heal – if there are medial expertise in your county/city to assist then a follow-up appointment in Singapore should be taken 6 weeks after surgery.
- A minimal week stay in Singapore:
- Check with Dynamic x-ray –
- Spinal Injection
- Procedure in between conservative and surgery
-
Pre-op and Post-Op Care
-
-
-
-
- Pre-operative
- If the patient is on blood thinners, they would have to stop 5 days before surgery
- Older patients need surgical clearance through blood tests
- Postoperative
- When the wound is healed, spinal stabilization exercises with a physiotherapist
- Core strengthening with a physiotherapist
- Pre-operative
-
-
-
Book an Appointment for surgery
Pinnacle Spine and Scoliosis Centre
web: www.p-ortho.com
Whatsapp: +65 9771 8964
Telephone: +65 6737 0680
Book an appointment for Physiotherapy
Physioactive Singapore
Web: www.physioactive.sg
Physioactive Indonesia
Web: www.physioactive.id/appointment
Whatsapp: +62 811 8897970